Linked Lists
Table of Contents
1. Linked Lists
A linked list is a way to represent a data sequence. A linked list is either empty or a first value and a pointer to the rest of the linked list. For example, to represent the sequence 3, 4, 5, the structure of the linked list would be:
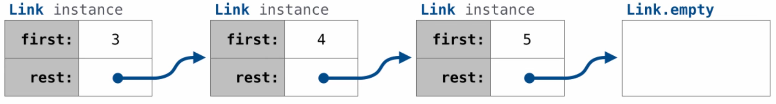
Each node of a linked list, then, is a pair: first, which is the value of its own element, then rest, which points to the next node in the rest of the linked list.
1.1. Implementation
Here is an implementation of a linked list class:
class Link:
empty = ()
def __init__(self, first, rest=empty):
assert rest is Link.empty or isinstance(rest, Link)
self.first = first
self.rest = rest
Example: Range, map, and filter for linked lists
We want to implement our own range_link, map_link, and filter_link functions for our linked list implementation. To do this, we will often need to use recursion:
def range_link(start, end):
if start >= end:
return Link.empty
else:
return Link(start, range_link(start + 1, end))
def map_link(f, s):
if s is Link.empty:
return s
else:
return Link(f(s.first), map_link(f, s.rest))
def filter_link(f, s):
if s is Link.empty:
return s
filtered_rest = filter_link(f, s.rest)
if f(s.first):
return Link(s.first, filtered_rest)
else:
return filtered_rest